本文共 3004 字,大约阅读时间需要 10 分钟。
region_proposal_cat.png
高斯反向投影
在图像处理中,我们通常需要设置感兴趣的区域(ROI,region of interest),来简化我们的工作。也就是从图像中选择的一个图像区域,这个区域是我们图像分析所关注的重点。
在上一篇文章图像相似度比较和检测图像中的特定物中,我们使用直方图反向投影的方式来获取ROI,在这里我们采用另一种方式高斯反向投影。它通过基于高斯的概率密度函数(PDF)进行估算,反向投影得到对象区域,该方法可以看成是最简单的图像分割方法。
随机变量X服从一个数学期望为μ、标准方差为σ2的高斯分布,记为:X∼N(μ,σ2),
则其概率密度函数为
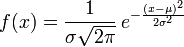
高斯分布的概率密度函数
其中,正态分布的期望值μ决定了其位置,其标准差σ决定了分布的幅度。
算法实现
输入模型M,对M的每个像素点(R,G,B)计算SUM=R+G+B
r=R/SUM, g=G/SUM, b=B/SUM
根据得到权重比例值,计算得到对应的均值 与标准方差
对输入图像的每个像素点计算根据高斯公式计算P(r)与P(g)的乘积
归一化之后输出结果,显示基于高斯分布概率密度函数的反向投影图像。
GaussianBackProjection的算法实现:
import com.cv4j.core.datamodel.ByteProcessor;
import com.cv4j.core.datamodel.ImageProcessor;
import com.cv4j.exception.CV4JException;
import com.cv4j.image.util.Tools;
public class GaussianBackProjection {
public void backProjection(ImageProcessor src, ImageProcessor model, ByteProcessor dst) {
if(src.getChannels() == 1 || model.getChannels() == 1) {
throw new CV4JException("did not support image type : single-channel...");
}
float[] R = model.toFloat(0);
float[] G = model.toFloat(1);
int r = 0, g = 0, b = 0;
float sum = 0;
int mw = model.getWidth();
int mh = model.getHeight();
int index = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < mh; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < mw; col++) {
index = row*mw + col;
b = model.toByte(2)[index]&0xff;
g = model.toByte(1)[index]&0xff;
r = model.toByte(0)[index]&0xff;
sum = b + g + r;
R[index] = r / sum;
G[index] = g / sum;
}
}
// 计算均值与标准方差
float[] rmdev = Tools.calcMeansAndDev(R);
float[] gmdev = Tools.calcMeansAndDev(G);
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
// 反向投影
float pr = 0, pg = 0;
float[] result = new float[width*height];
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
index = row*width + col;
b = src.toByte(2)[index]&0xff;
g = src.toByte(1)[index]&0xff;
r = src.toByte(0)[index]&0xff;
sum = b + g + r;
float red = r / sum;
float green = g / sum;
pr = (float)((1.0 / (rmdev[1]*Math.sqrt(2 * Math.PI)))*Math.exp(-(Math.pow((red - rmdev[0]), 2)) / (2 * Math.pow(rmdev[1], 2))));
pg = (float)((1.0 / (gmdev[1]*Math.sqrt(2 * Math.PI)))*Math.exp(-(Math.pow((green - gmdev[0]),2)) / (2 * Math.pow(gmdev[1], 2))));
sum = pr*pg;
if(Float.isNaN(sum)){
result[index] = 0;
continue;
}
result[index] = sum;
}
}
// 归一化显示高斯反向投影
float min = 1000;
float max = 0;
for(int i=0; i
min = Math.min(min, result[i]);
max = Math.max(max, result[i]);
}
float delta = max - min;
for(int i=0; i
dst.getGray()[i] = (byte)(((result[i] - min)/delta)*255);
}
}
}
GaussianBackProjection的具体使用
GaussianBackProjection gaussianBackProjection = new GaussianBackProjection();
gaussianBackProjection.backProjection(colorProcessor,sampleProcessor,byteProcessor);
result.setImageBitmap(byteProcessor.getImage().toBitmap());
其中,colorProcessor表示原图的对象,sampleProcessor是选取区域的对象,byteProcessor表示反向投影结果。最终byteProcessor把结果展示到Android的ImageView上。
高斯反向投影.png
总结
cv4j 是gloomyfish和我一起开发的图像处理库,纯java实现,目前的版本号是0.1.1
前段时间工作比较繁忙cv4j系列停更了一段时间,这次回来我们修复了一些bug。
上一篇cv4j系列的文章讲述了直方图投影,这次的高斯反向投影是另外一种选择。其实,模版匹配也能在图像中寻找到特定的目标,接下来我们的cv4j也会开发模版匹配的功能。
转载地址:http://skifa.baihongyu.com/